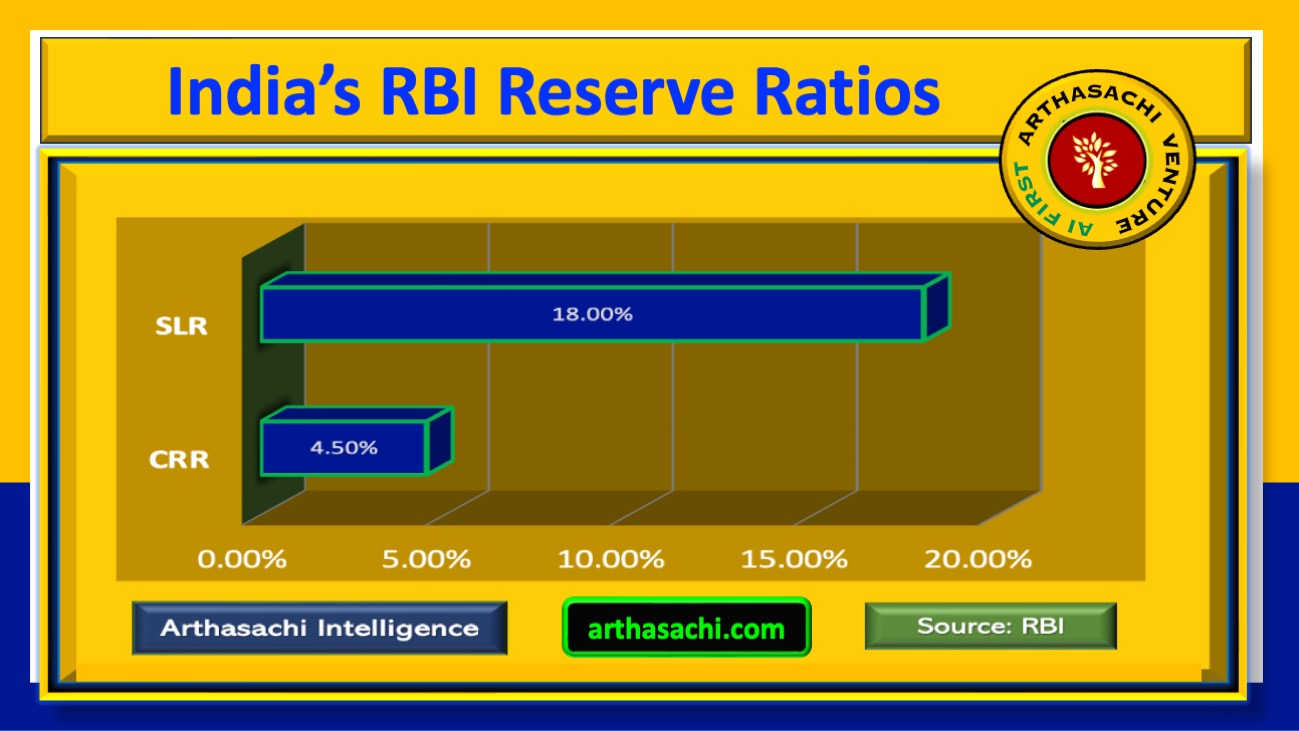
RBI Reserve Ratios ( CRR & SLR )
Reserve Bank of India (RBI), the Central Bank regulate the banking system in India through the provisions of the Banking Regulation Act, 1949.
One the primary functions of RBI is to control the supply as well as cost of credit. In common language, it means how much money is available for the industry or the economy and the price that the economy has to pay to borrow that money which is commonly called in banking term liquidity and interest rate. RBI with its Monetary Policy and various quantitative tools provide direction to control money supply in the economy to fight against inflation and deflation situation. CRR and SLR are the ratios
CASH RESERVE RATIO ( CRR )
RBI as a Central Bank it requires all the banks to maintain a certain portion of Deposits in the form of a cash. This portion or percentage of liquid cash is to be maintained with RBI and is referred to as CASH RESERVE RATIO.
STATUTORY LIQUIDITY RATIO ( SLR )
SLR (Statutory Liquidity Ratio) is the money a commercial bank needs to preserve in the form of cash, or gold or government authorized securities (Bonds) before providing credit to their own customers. SLR rate is decided by the RBI (Reserve Bank of India) as well as to control the expansion of bank credit.


