RBI Monetary Policy: Repo rate cut by 25 Bp, GDP growth forecast at 6.7% for FY26
On February 7, 2025: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) released its Monetary Policy Statement for February 5-7, 2024-25, delivered by Governor Sanjay Malhotra.
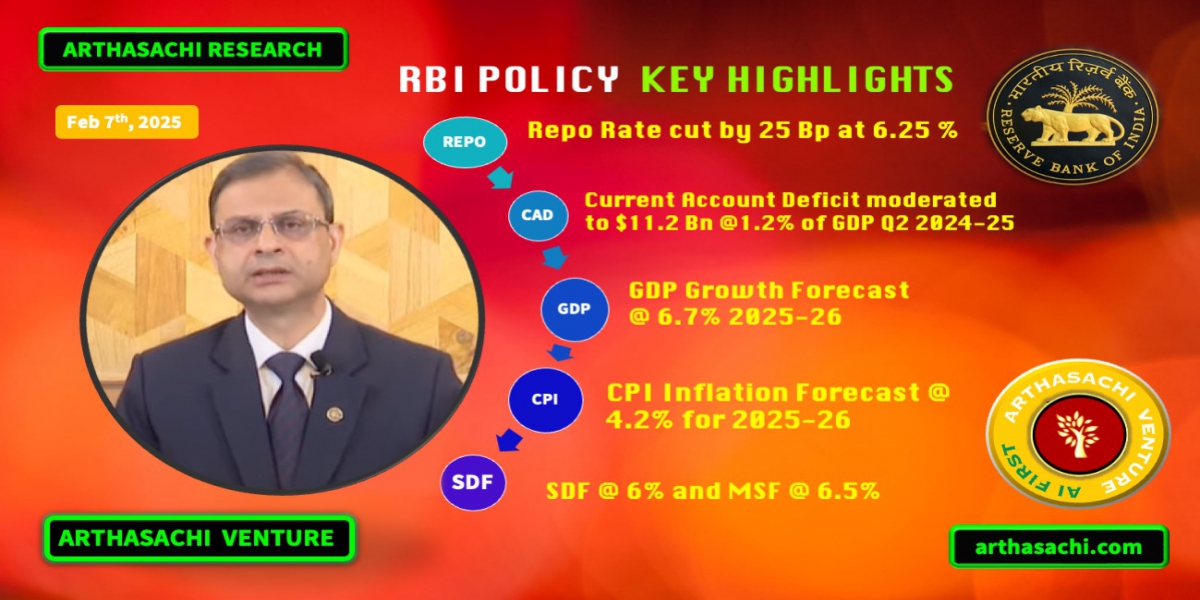
In its first monetary policy meeting RBI Governor Sanjay Malhotra cut the repo rates by 25 Basis point to 6.25% and GDP forecast for 2025-26 at 6.7%. The Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) outlined key decisions, economic projections, and regulatory measures aimed at navigating India's economy through a complex global landscape while fostering growth, stability, and consumer protection. Below is a summary and the key highlights from the policy announcement.
Summary
- Benchmark policy repo rate cut by 25 basis points to 6.25%
- GDP growth forecast for 2025-26 at 6.7%
- Inflation forecast at 4.2% for 2025-26, assuming a normal monsoon.
- Maintained its neutral stance, under tremendous global uncertainties
Key Highlights
1. Policy Rate Cut and Neutral Stance Retained
The MPC unanimously decided to reduce the policy repo rate by 25 basis points, bringing it down from 6.50% to 6.25%. Consequently, the Standing Deposit Facility (SDF) rate adjusted to 6.00%, and the Marginal Standing Facility (MSF) rate and Bank Rate aligned at 6.50%. Despite the rate cut, the MPC maintained its neutral stance, emphasizing a focus on aligning inflation durably with the target of 4% (within a 2-6% tolerance band) while supporting economic growth. The rationale behind this decision was a noted decline in inflation and the need for a less restrictive monetary policy given current growth-inflation dynamics.
2. Economic Growth Projections
As per the first advance estimates, real GDP growth for the current year is estimated at 6.4%, a softer expansion after a robust 8.2% growth last year. The RBI projected real GDP growth for 2025-26 at 6.7%, reflecting resilience in the Indian economy despite global headwinds. Quarterly estimates are as follows:
- Q1: 6.7%
- Q2: 7.0%
- Q3: 6.5%
- Q4: 6.5%
The outlook is supported by improving rural demand, healthy agricultural activity, and buoyancy in services exports. However, risks from global uncertainties, including geopolitical tensions and trade volatility, remain a concern.
3. Inflation Outlook
CPI inflation for the current financial year (2024-25) is projected at 4.8%, with Q4 expected at 4.4%. For 2025-26, assuming a normal monsoon, inflation is forecasted at 4.2%, with quarterly projections of:
- Q1: 4.5%
- Q2: 4.0%
- Q3: 3.8%
- Q4: 4.2%
The moderation in headline inflation (from 6.2% in October 2024 to 5.2% in December 2024) is attributed to softening food prices, good kharif production, and favorable rabi crop prospects. However, upside risks from global financial market volatility and energy price fluctuations persist.
4. Reflection on Flexible Inflation Targeting (FIT)
Governor Malhotra highlighted the success of the FIT framework, adopted in 2016 and reviewed in 2021. The framework has kept average inflation lower and largely aligned with the target, despite occasional breaches during the post-pandemic period. The RBI plans to further refine this framework by leveraging new data, improving forecasting models, and responding to evolving economic dynamics.
5. Global Economic Context and External Sector Resilience
The global economy continues to grow below its historical average (3.3% projected for 2025-26 per the IMF, against a 3.7% average), with challenges including stalled disinflation, capital outflows from Emerging Market Economies (EMEs), and a stronger US dollar. India, however, remains resilient. The current account deficit (CAD) moderated to US$ 11.2 billion 1.2% of GDP in Q2 2024-25 from 1.3% of GDP in Q2 of last year, and foreign exchange reserves stood at US$630.6 billion as of January 31, 2025, providing over 10 months of import cover. The RBI reiterated its exchange rate policy of maintaining stability without targeting specific levels.
6. Liquidity and Financial Market Measures
System liquidity shifted from surplus to deficit in December 2024 and January 2025 due to advance tax payments in December 2024, capital outflows, forex operations and increased currency circulation. The RBI urged banks to actively participate in the uncollateralized call money market to enhance depth and improve signaling through the weighted average call money rate (WACR). Measures like Variable Rate Repo auctions and open market operations (OMOs) have been deployed to ensure sufficient liquidity.
7. Regulatory and Digital Initiatives
- Digital Security: To combat rising cyber threats, the RBI will extend Additional Factor of Authentication (AFA) to international digital payments made to offshore merchants and introduction of AFA for domestic digital payments. RBI also introduce exclusive domains ('bank.in' and 'fin.in') for banks and financial sector this will help avoid banking fraud starting April 2025.
- Government Securities Market: Forward contracts in government securities will be introduced to help long-term investors such as insurance funds to manage interest rate risks, also enable efficient pricing of derivatives that use Gov. securities as underlying instruments. Alongside these changes expanded access to the NDS-OM platform for SEBI-registered non-bank brokers.
- Market Timing Review: A working group will review trading and settlement timings across across various market segments, with a report due by April 30, 2025.
8. Financial Literacy and Inclusion
The RBI’s annual Financial Literacy Week, starting February 24, 2025, will focus on "Financial Literacy: Women’s Prosperity," emphasizing women’s role in financial decision-making and household budgeting.
9. Financial Stability
Scheduled Commercial Banks (SCBs) and Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) exhibit healthy financial parameters. The Credit-Deposit ratio stood at 80.8% as of January 2025, with robust returns on assets (RoA) and equity (RoE), despite a moderated net interest margin (NIM).
India can achieve 7% plus growth rate, and we should aspire for that, said RBI Governor Sanjay Malhotra. He added, “The uncertainty in itself is worrisome, that has a direct impact on growth, investment decisions and consumption expenditure that get deferred.”
Conclusion: Striking the Right Balance
The RBI’s February 2025 monetary policy reflects a pragmatic approach to fostering economic growth while managing inflation and ensuring financial stability. The 25-basis-point rate cut signals a shift toward supporting growth amid moderating inflation, while the neutral stance underscores the MPC’s readiness to adapt to future developments. With a slew of regulatory and digital measures, the RBI aims to bolster resilience against global uncertainties and digital risks, positioning India’s financial system for sustained progress. As a RBI Governor Sanjay Malhotra emphasized, the central bank remains committed to timely, calibrated, and well-communicated actions to reinforce macroeconomic stability.
This policy underscores the RBI’s delicate balancing act—navigating domestic priorities against a turbulent global backdrop—while laying the groundwork for a robust and inclusive financial future.
Top News
Other News
MARKETS
WEALTH
ECONOMICS
START UP
TECHNOLOGY
BUSINESS
Alliances and Partners

Arthasachi Venture Footprints